Translation tools aren’t new—tools like Google Translate have been around for over a decade by now. In fact, depending upon the language, Google translate can be incredibly accurate. Take a look at the results of this study carried out by the
UCLA Medical Center, which found that tool was overall 82.5% accurate in conveying meaning across languages.
For really common translations, like English to Spanish, it’s hard to beat the classics. But, what about AI?
Can I use AI to translate text?
You can absolutely use AI tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT or Google’s Gemini to translate content. However, the comparison here isn’t exactly apples to oranges.
Google Translate supports a staggering 133 languages, while ChatGPT
only supports 85 as of writing. That means if you’re hoping to translate to, from, or between any of those 48 languages then AI may not be right for you.
However, what AI lacks in support it more than makes up for in potential. The conversational capabilities and advanced language understanding of modern AI tools makes it possible to generate far more accurate results—with the right prompting of course.
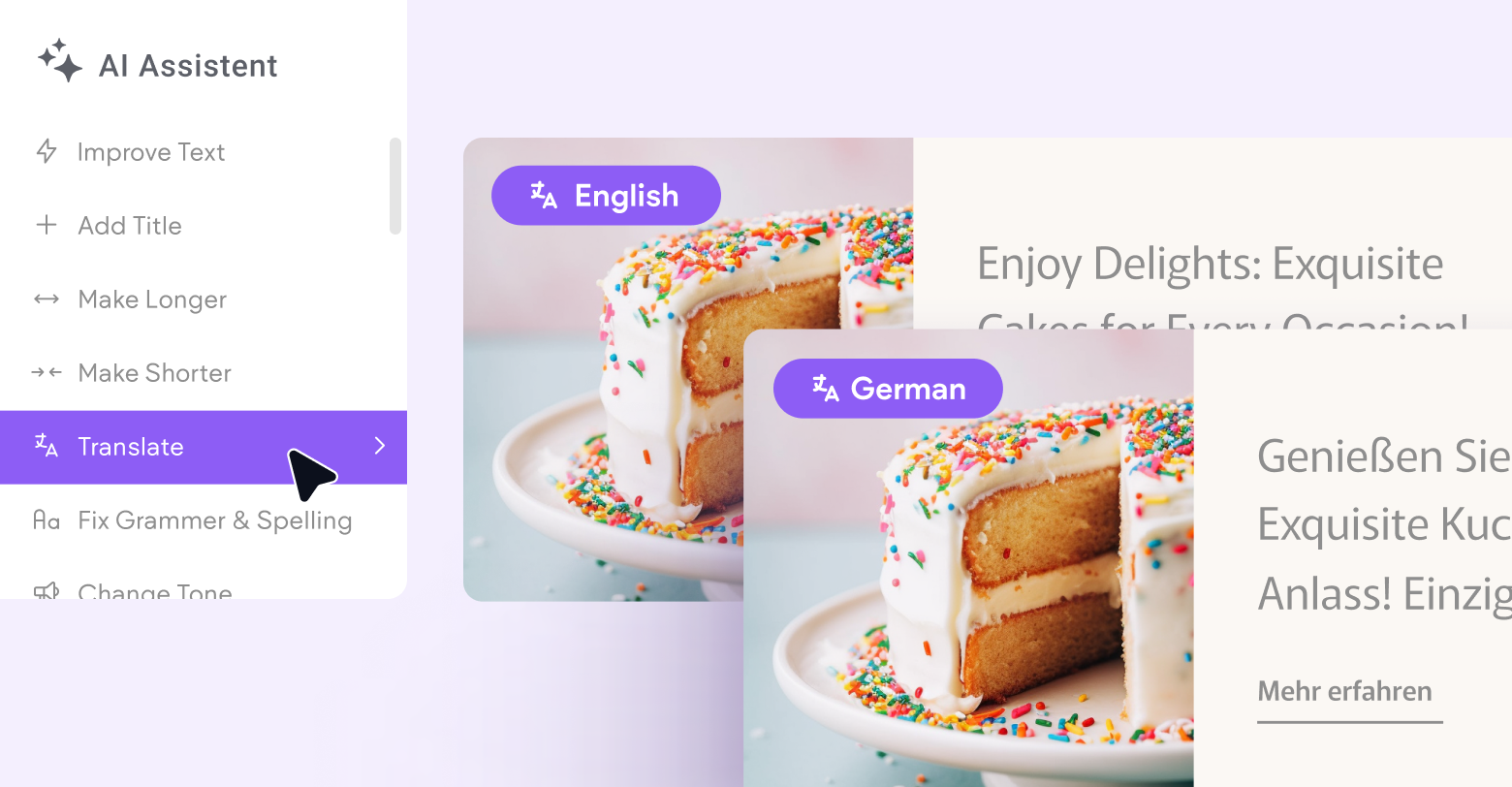
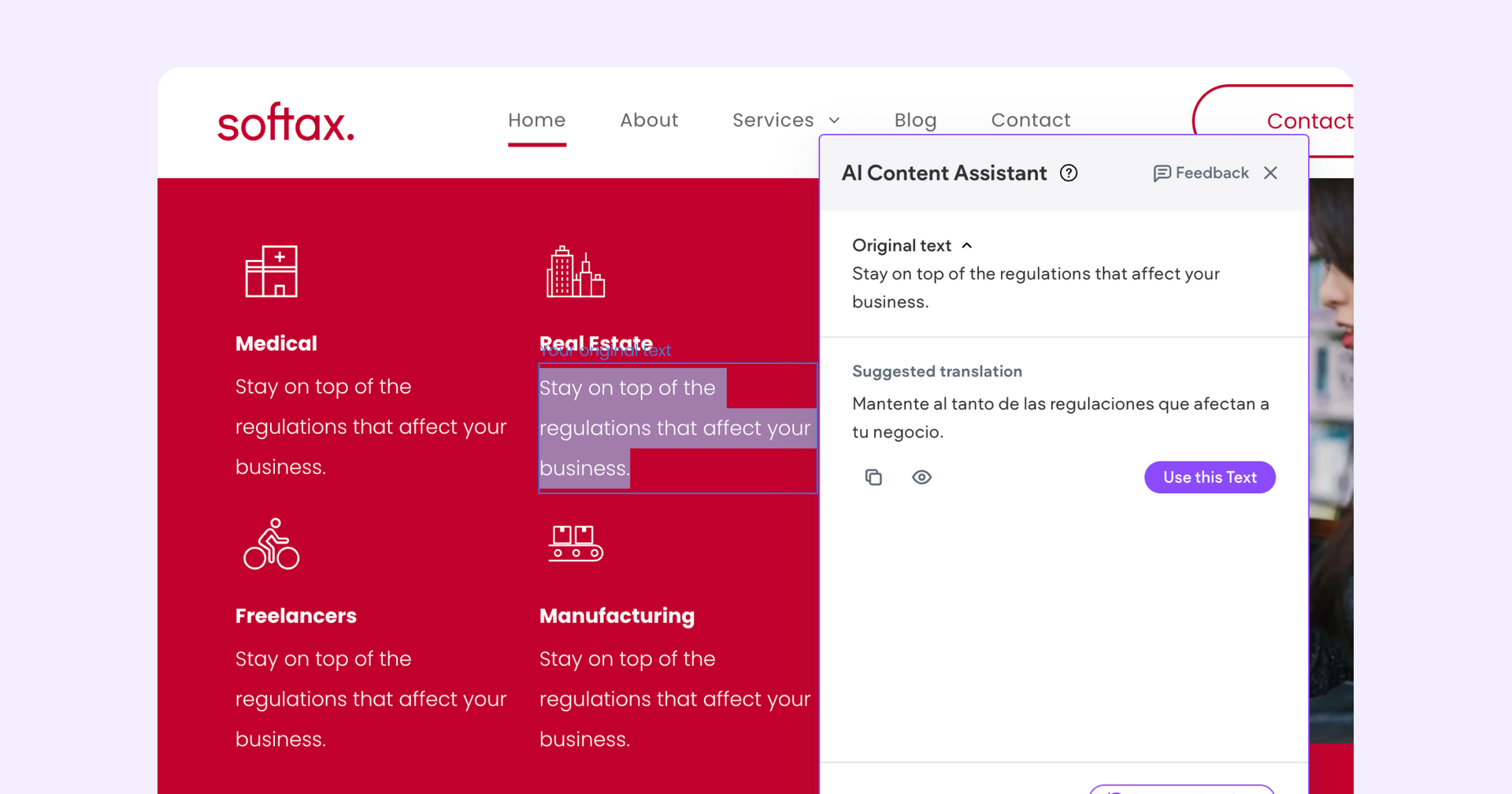
A quick, shameless plug before we dive into the finer points of translation prompting—if you don’t want to deal with this you don’t have to. Duda’ AI Assistant supports translation out of the box for many common languages. Just highlight your text in the editor, select the AI Assistant, then scroll down to “Translate.”
If you want to make your entire site multilingual, that process is
even more automatic.
How to prompt for content translation
Writing translation prompts for AI is a lot like
writing any prompt for AI—it’s all about being specific. This is especially true for translations. Languages are complex and heavily dependent upon context, context that you need to express within your prompting.
The ability to recognize contextual nuance is the pivotal difference between AI and a non-conversational tool like Google Translate. Take the following prompt, for example:
Because you instructed the AI to speak as if it is a native of the target language, this phrasing should attempt to maintain as many cultural connotations as possible in the translation.
This example works a little differently by explicitly stating the context of the conversation being discussed. This is useful for situations where text is heavy in metaphor or technical in nature.
You can also specify the format the text is in, such as a poem or a song, to ensure that format is maintained in the translation.
Why not combine prompts? You can simplify content while translating simultaneously by specifying the style of the content. Here’s one example:
Context elevates your translations
From the examples above, you can start to see the benefit of using AI to translate and localize your content—the conversational nature of these tools. Consider a metaphor like “it’s raining cats and dogs,” as an example. You could directly translate that to "está lloviendo gatos y perros,” however, while technically correct, that phrase does not convey the same meaning as the English version. "Está lloviendo a cántaros," instead, better conveys the same meaning even though it isn’t a direct translation.
That example is a situation that modern day translation tools, like Google Translate, are smart enough to catch—given how commonplace the phrase is. However, more niche language, especially industry jargon, may benefit significantly from the additional context available to AI tools.
Have you experimented with using AI to translate your content? Some agencies might be fearful of SEO repercussions resulting from publishing AI-generated content, but don’t worry, we’ve
already written about that.